The Bottom Line: The lowest expense ratio index tracking sustainable ETFs largely pursue an ESG screening strategy with exclusions, followed by funds with climate-oriented objectives.
Notes of explanation: Sources: Morningstar Direct, fund prospectuses and Sustainable Research and Analysis LLC.
Observations:
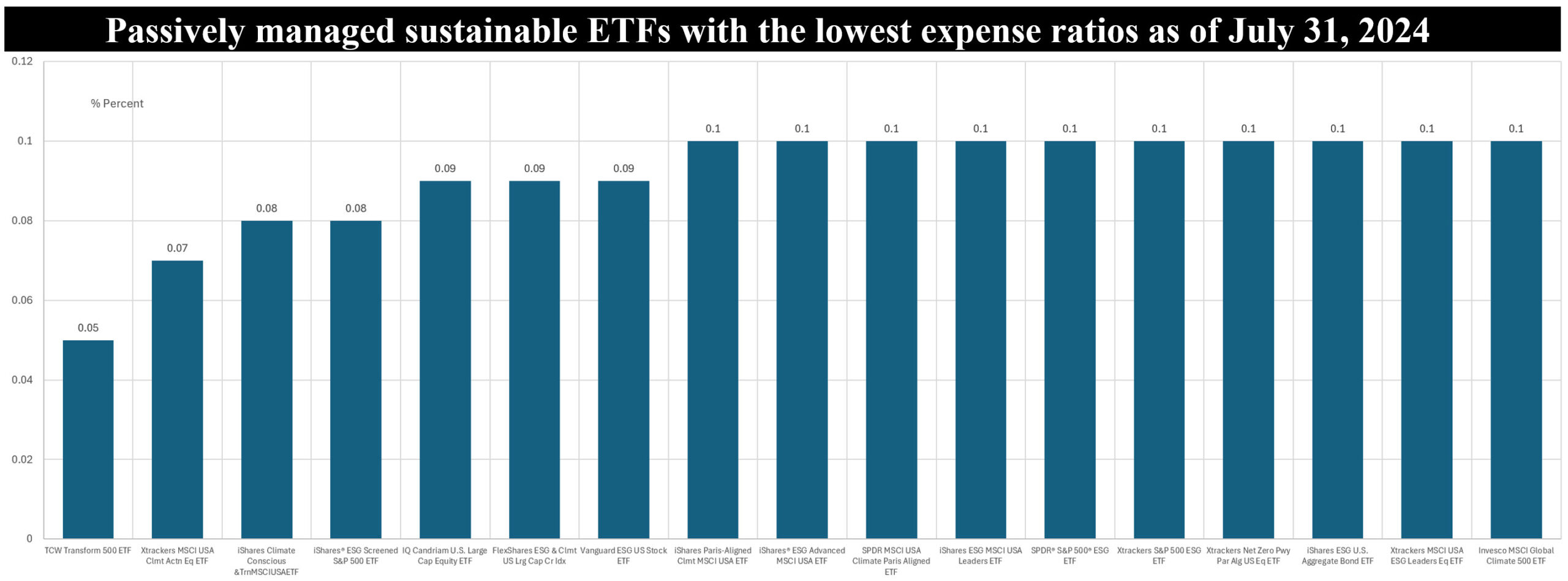
• Passively managed sustainable ETFs with the lowest expense ratios largely consist of equity-oriented funds but also include one fixed income fund. These funds, a total of 17 ETFs, levy expenses that translate into expense ratios ranging from a low of 0.05% attributable to the TCW Transform 500 ETF to 0.1% reported by ten funds. The average expense ratio attributable to these 17 funds, including 10 funds with the same 0.1% expense ratio, is .09%.
• More broadly, the universe of passively managed sustainable ETFs is comprised of 155 funds with $96.6 billion in assets under management as of July 31, 2024. These funds maintain an average expense ratio of 0.34%, with a range that extends from 0.05% to 0.93% reported by the levered Direxion Daily Electric and Autonomous Vehicles Bull 2X Shares. The median expense ratio for the broader universe is 0.26%
• By way of comparison, actively managed sustainable ETFs carry an average expense ratio of 0.53%. The smaller segment of 85 funds with $9.8 billion in assets under management, reports expense ratios that range from a low of 0.14% (excluding one actively managed ETF with an expense ratio of zero) to a high of 1.0%.
• The largest number of passively managed sustainable ETFs with the lowest expense ratios pursue an ESG screening strategy that’s combined with exclusions, followed by funds with a climate-oriented objective. The fund with the lowest expense ratio, the 0.05% TCW Transform 500 ETF, tracks the performance of the Morningstar US Large Cap Select Index which measures the performance of the 500 largest U.S. stocks by market capitalization, as determined by Morningstar, Inc. At the same time, the fund seeks to encourage accountability, change acceleration or transformational change at the public companies within its portfolio specifically through the application of proxy voting guidelines and through dialogue with management of the portfolio companies.
• ESG screening involves an emphasis on ESG scores or some other metrics to qualify the eligibility of securities, such as stocks or bonds, and use these as a basis for overweighting, underweighting or, in some cases, optimizing their exposures in a portfolio.