The Bottom Line: Green bond funds, which have performed well over the last five years, offer a compelling thematic sustainable investment option in bond allocations.
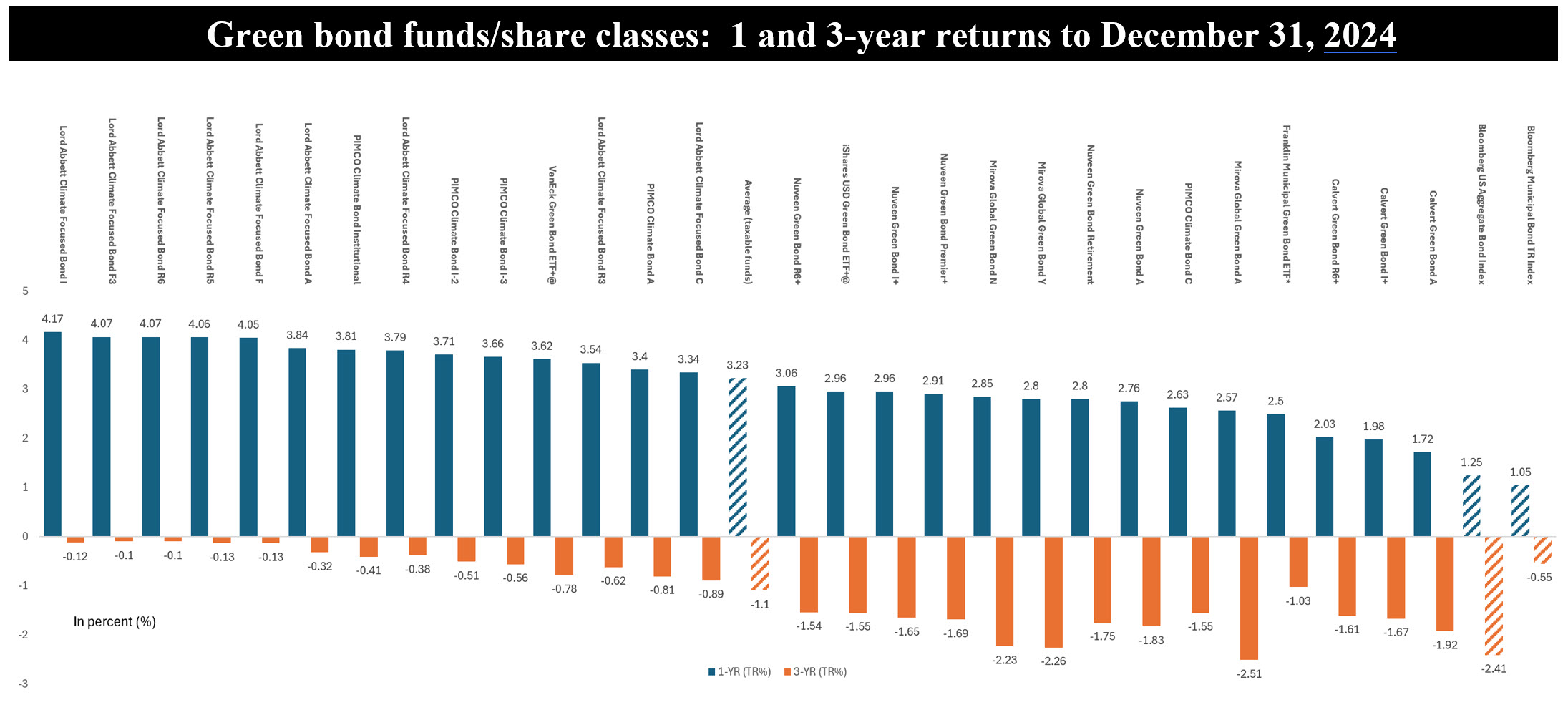
Notes of Explanation: Funds/share classes listed in order of total return performance in 2024. 3-year returns are average annual. + refers to the most highly rated funds (A rated) based on scoring by Sustainable Research and Analysis. @refers to index fund. Sources: Sustainable Research and Analysis LLC.
Observations:
• Green bond funds, both taxable and municipal, that invest in green bonds, ended YE 2024 with $1,660.2 million in total net assets, versus $1,500.5 million at the end of 2023. The year-over-year increase of $159.70 million, or 11%, is juxtaposed against an increase of $2.8 billion, or a 6%, posted by sustainable bond funds more generally, including taxable and municipal bond funds, that ended 2024 with $49.5 billion in net assets. The year-end assets under management by green bond funds also represents a high-water mark for the green bonds segment.
• With the addition of one new green bond fund that was launched in 2024, namely the Carbon Collective Short Duration Bond ETF, the universe of green bond funds now includes nine funds/29 share classes, consisting of both taxable and municipal, actively managed as well as passive mutual funds and ETFs. Four firms manage the largest funds which account for 87% of the segment’s assets. These are Calvert, BlackRock’s iShares, Nuveen and VanEck that together manage $1.4 billion in assets. The $101.6 million Franklin Municipal Green Bond ETF, a municipal Federal tax-exempt fund that was rebranded in 2022 and has experienced limited growth, pushes the percentage up to 93%. Also, the segment’s investors is dominated by institutional investors that make up a minimum of $889.4 million in assets, or 54% based strictly on designated institutional share classes.
• While the green bond funds segment is small and concentrated, it nevertheless offers investors an attractive thematic sustainable investment option that can be integrated into a portfolio’s bond allocation. Funds in this segment focus on investments that are selected based on their commitment to finance or refinance, in part or in full new and/or existing eligible climate and environmental projects while at the same time realizing market-based rates of return. Otherwise, these investments are identical to conventional bonds offered by the same firms. Some funds report on their environmental outcomes, in addition to mandated investment performance results. By their nature, these investment vehicles also present to investors the benefit of diversification and risk mitigation, two beneficial features as some investments in the environmental sphere can be risky. This was underscored last week when Ørsted, a Danish power and heat producer that generates over 90% of its energy from renewables and has financed a significant amount of its debt through the issuance of lower-end of the range investment-grade green bonds, announced yet another large impairment charge due to wind power project delays in the US and higher financing costs. As a result of its financial headwinds, the company’s stock price has dropped further, and its bonds have fluctuated in price. (Note: Ørsted’s green bonds which have been issued in EU and GDP have a small and very limited exposure within the nine funds that comprise the green bond funds universe.)
• 2024 was a challenging one for bonds as Fed policy changes contributed to a roller-coaster year for fixed income. In the end, performance was muted, with small gains being realized by higher-grade intermediate bonds. Bonds were up 1.25% according to the Bloomberg US Aggregate Bond Index. Against this backdrop, taxable green bond funds were up an average of 3.2%, or 2X greater than the broad-based bond benchmark. Over the previous three and five years, green bond funds, on average, also outperformed the same intermediate investment-grade benchmark.
• Of the nine green bond funds, four funds or 7 funds/share classes, including the Calvert Bond Fund (classes I and R6), iShares USD Green Bond ETF, Nuveen Green Bond Fund (classes I, Premier and R6), and VanEck Green Bond ETF are the most highly rated based on scoring by Sustainable Research and Analysis, based on a combination of the five screens that include management company quality, years in operation, total return performance over one, three and five years, expense ratio as well as fund size.