Sustainable institutional investors dominate in Europe and the US
According to data published by Eurosif in the latest European SRI 2018 Study that was released in November of 2018 , retail assets in Europe now account for 31% of sustainable investments, compared with just 3.4% in 2013 and 22% in 2015. At the same time, retail investors in Europe are expected to increase their allocation to sustainable investments from 38% of their portfolio today to 48% within the next five years. While exact comparisons are difficult to make, US SIF data released last year indicates that about $3.0 trillion or 26% of sustainable assets in the US are sourced to individual investors. At the same time, when viewed through the prism of sustainable mutual funds in the US, retail investors, at 62.1%, account for a much larger percentage of sustainable investment assets. That said, the percentage of institutional investors in funds and the drivers of growth in the sustainable US mutual funds segment in recent years are linked to institutional rather than retail investors. Regardless, it seems that in both the US and European jurisdictions, retail investors are motivated to invest sustainably but at the same time challenges exist and retail net cash inflows remain anemic. The key challenges to individual investors include some combination of a limited supply of suitable product offerings, the perception that investing pursuant to a sustainable mandate is subject to a negative trade-off with returns and a lack of understanding of the financial products offered to them. Both in Europe and the US, these hurdles could, in part, be overcome with increased emphasis on education and more transparent disclosures by investment managers to inform investor’s understanding of a fund’s sustainability goals, methods for achieving such goals and their achievements or impacts over time. Preferably, such disclosures should be provided in a way that allows investors to track, evaluate and also compare the range of outcomes across funds.
Retail investors in Europe: $7.4 trillion or 31% of managed assets
Based on its analysis of survey results collected from 263 participating asset managers and asset owners with combined assets under management of EUR 20 trillion, or US$23.9 trillion , representing by its own estimates market coverage of 79%, $7.4 trillion or 31% of invested assets allocated to sustainable strategies (including the following strategies: Exclusions or negative screening, norms-based screening, best-in-class investment section, thematic investing, ESG integration, engagement and proxy voting and impact investing) are sourced to retail investors. This level is increasing and compares to 22% in 2015 and 3.4% in 2013. Still, this is not fast enough for European regulators who are advocating legislative proposals that seek to create a green finance economy, improve disclosures and provide various investment tools for investors, with the end goal of stimulating sustainable investing by which to support funding the European transition to a sustainable and low-carbon economy.
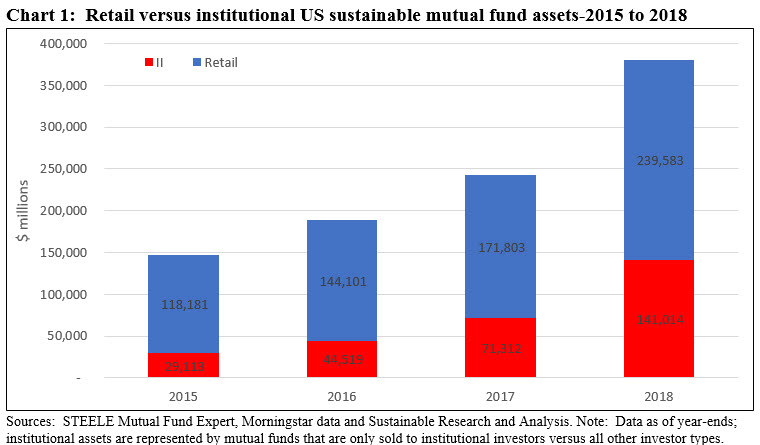
Retail investors in the US: Ranging from $3 trillion or 26% of managed assets to $239.6 billion or 62.1% of mutual fund assets
US SIF survey data collected from 365 money managers and 1,145 community investment institutions and released last year indicates that about $3.0 trillion or 26% of sustainable assets in the US are sourced to individual investors . This information is derived from manager survey responses and while the ultimate beneficiaries may be individual investors, they may not be involved in the actual decision making. Another perspective may be drawn from the universe of active and passively managed designated sustainable US mutual funds and their corresponding share classes that stood at $390.4 billion in assets under management at year-end 2018. This approach shows that sustainable assets sourced to retail and institutional investors have both been expanding, but institutional assets have been gaining assets at a much more rapid pace. In contrast to European and US SIF data, 62.1% of sustainable mutual fund assets are sourced to retail investors as of year-end 2018. But the percentage of retail assets has been declining in recent years. Refer to Chart 1. This is due to several factors, starting with the increasing traction gained by institutional investors in sustainable investing, including investors such as public pension funds, endowments, foundations and insurance companies, to mention just a few. Second, retail net cash inflows into sustainable investment vehicles are still modest. Third, the trend among mainstream managers to repurpose existing funds by adding sustainable investing strategies to existing product offerings. The strategy of repurposing has impacted a large number of institutional only funds, as demonstrated in 2018 by the rebranding of institutional funds managed by Aberdeen Investments, JP Morgan and Morgan Stanley, in particular. As a consequence, the number of funds and assets under management geared to institutional investors have expanded significantly. Institutional only funds expanded by 384% over the last four years and now account for 37.1% of assets.
Education, as well as improved reporting and disclosure, would serve to motivate and inform the investment choices made by individual investors
In addition to education, improved reporting and disclosure would serve to motivate and inform the investment choices made by individual investors. Reporting and disclosure practices are continuing to evolve but, in the end, investors in explicitly designated sustainable investment funds, both actively managed as well as passively managed investment vehicles, should be offered transparent disclosures that clarifies their understanding of a given fund or portfolio’s sustainability strategies and approaches as well as achievements or impacts. Such disclosures should allow investors to track, evaluate and also compare the range of outcomes across funds.
To this end, the following information should be offered and available to investors:
(1) The approach and methodologies used to integrate sustainability practices into the investment management process.
(2) Information about how the sustainable methodologies have impacted decisions to include, exclude and weight companies, if applicable, based on the methodologies used. Explanations, illustrations and case studies are useful.
(3) Portfolio performance focused on targeted sustainability and ESG objectives. Standards for assessment are evolving, are lacking or these are in the early stages of development and may not be available as yet across all impact areas. Still, investor oriented annual fund specific reports should become common practice. These should describe and quantify the impacts achieved by the fund and its investments, using relevant and material metrics along with relevant explanations and assumptions.
(4) Shareholder engagement activities and outcomes, if any, and proxy voting records.