The Bottom Line: J. P. Morgan’s sustainable target date SmartRetirement Fund expands to four the number and variety of available target date options for investors.
J.P. Morgan is latest manager to move into the sustainable target date funds space
J.P. Morgan Investment Management is the latest manager to move into the sustainable target date funds space, having posted on December 23, 2021 prospectus amendments to onboard the consideration of certain environmental, social and governance (ESG) factors in the investment process applicable to the to the JPMorgan SmartRetirement Fund prospectuses. Like the other offerings in the segment, the JPMorgan SmartRetirement Fund is organized as a “fund of funds” with each target date fund investing in J. P. Morgan mutual funds as well as ETFs. These underlying funds are actively managed investment vehicles that employ ESG integration strategies. Having commenced operations in 2008 the portfolio of nine target date funds ranging from 2020 to 2060 target dates, offering eight share classes each, have attracted $34.5 billion in assets under management as of year-end 2021. This latest sustainable target date fund addition expands to four the number and variety of available target date options that now stand at $40.1 billion in assets under management, including the JPMorgan SmartRetirement Fund assets. Investors now have a broader range of structures, sustainable strategies, and pricing alternatives to choose from, as described in Table 1.
Target date funds, sometimes also referred to as lifecycle funds, are most used for long-term retirement or education savings, including default options in corporate 401(k) plans
Target date funds, sometimes also referred to as lifecycle funds, are most used for long-term retirement or education savings where the owner of the account expects to use the proceeds at a known future date. They are designed to satisfy an investor’s investment objective by a particular target date, which is usually included in the name of the fund. For example, the JPMorgan SmartRetirement 2060 Fund is designed for persons who plan to retire in around 38 years. To fulfill the investor’s investment objective, the fund is typically constructed as a hybrid fund that follows a predetermined reallocation of risk over the lifetime of the investment pursuant to a glide path that charts the fund’s strategic target allocations among a mix of asset and sub-asset classes. The fund’s strategic target allocations generally become more conservative as the target retirement date approaches. In the case of the JPMorgan SmartRetirement 2060 Fund, the portfolio today is constructed around a strategic asset allocation consisting of a 91% exposure to equities and 9% to fixed income funds or securities. Included in these categories are various sub-groups of equities and fixed income securities. In contrast, a fund with a target date of about five years from today is constructed with a 48.50% exposure to equities and 51.50% investment in fixed income securities. Refer to Table 2 for JPMorgan’s current strategic asset allocation across the various target date funds. Interestingly, it is being debated today whether allocations to equities at or around retirement dates are too conservative and should be lifted above the 50% or so level for investors who can tolerate higher risk and can afford to do so based on their circumstances. This is not an inconsequential point, as target date funds have become a dominant investment default option in many corporate 401(k) retirement plans.
Investors now have another sustainable investing option to consider
As part of its active management investment assessment, J.P. Morgan considers the risks presented by certain environmental, social and governance factors. Specifically, the adviser will assess how ESG risks are considered within an active underlying fund’s/manager’s investment process and how the active underlying fund/manager defines and mitigates material ESG risks. This approach to sustainable investing gives investors another sustainable investing option to consider as it contrasts with the ESG screening and exclusions index tracking approach employed by BlackRock, the values-based strategy employed by GuideStone Capital Management and the more varied combination approach that includes ESG integration, exclusions and thematic investing offered by Natixis Advisors. That said, investors must also consider each firm’s fundamental investment approach, glide path philosophy, fund expenses and historical performance results, to mention some of the other key evaluation factors that are expected to influence performance outcomes.
Fund performance results are largely influenced by a fund’s strategic asset allocation, based on its glide path, and fund expenses. In 2021, returns across the four target date funds ranged from a low of 7.6% to a high of 10.7% for the more conservatively managed 2025 target date portfolios. At the other end of the range, funds with 2060 target dates with their 90%+ allocation to equities posted returns ranging from 16.4% to 20%.
Table 1: Sustainable target-date funds and their sustainable investment strategies
Investment Manager/Fund | Fund Structure | Start Year | Assets ($M) | Expense Ratios | Sustainable Investment Strategy |
BlackRock Fund Advisors/ BlackRock LifePath ESG Index Fund | Largely affiliated sustainable passively managed ETFs but also some mutual funds in a fund of funds like structure with target dates from 2025 to 2065 as well as a Retirement fund option. | 2020 | 28.1 | Range from 25% to 0.50%, depending on share class. | ESG screening and exclusions. Much of the investable universe consists of securities managed in the form of index tracking funds that optimize higher ESG ratings, subject to maintaining risk and return characteristics like the underlying index, after factoring in exclusions base on business practices and severe business controversies. A limited number of funds do not pursue ESG mandates, for example, iShares Developed Real Estate Index Fund. |
GuideStone Capital Management, LLC/ GuideStone Funds MyDestination Fund | Affiliated underlying active and passively managed mutual funds ranging in target dates from 2015-2055 that are advised by external independent investment managers. | 2006 | 5,519.0 | Range from 0.50% to 0.75%, depending on share class. | Values-based/Exclusions. Funds may not invest in any company that is publicly recognized, as determined by GuideStone Financial Resources of the Southern Baptist Convention, as being in the alcohol, tobacco, gambling, pornography or abortion industries, or any company whose products, services or incompatible activities. |
J.P. Morgan Investment Management/ JPMorgan SmartRetirement Fund | Primarily invest in other J. P. Morgan mutual funds as well as ETFs. Target dates range from 2020 to 2060. | 2021 | 34,453.5 | Range from 0.56% to 0.65%, depending on maturity and share class. | ESG Integration. The adviser will assess how ESG risks are considered within an active underlying fund’s/manager’s investment process and how the active underlying fund/manager defines and mitigates material ESG risks. Although these risks are considered, underlying funds and securities of issuers presenting such risks may be purchased and retained by the fund. |
Natixis Advisors, L.P. (a unit of Natixis, a French-based firm)/Natixis Sustainable Future Fund | Affiliated underlying actively managed mutual funds ranging in target dates from 2015-2060 that are advised by affiliated investment managers (examples include Loomis Sayles and Harris Assoc.). | 2017 | 103.6 | Range from 0.55% to 0.60%, depending on share class. | ESG Integration, Exclusions and Thematic Investing. Implementation of ESG strategies may vary across underlying funds. Certain ESG strategies may also seek to exclude specific types of investments. Range of underlying funds also includes thematic funds, such as funds investing in green bonds or carbon neutrality. |
Sources: Fund prospectus and related materials. Assets as of December 31, 2021. Sources: Morningstar Direct and Sustainable Research and Analysis.
Table 2: J.P. Morgan’s current strategic asset allocation across the various target date funds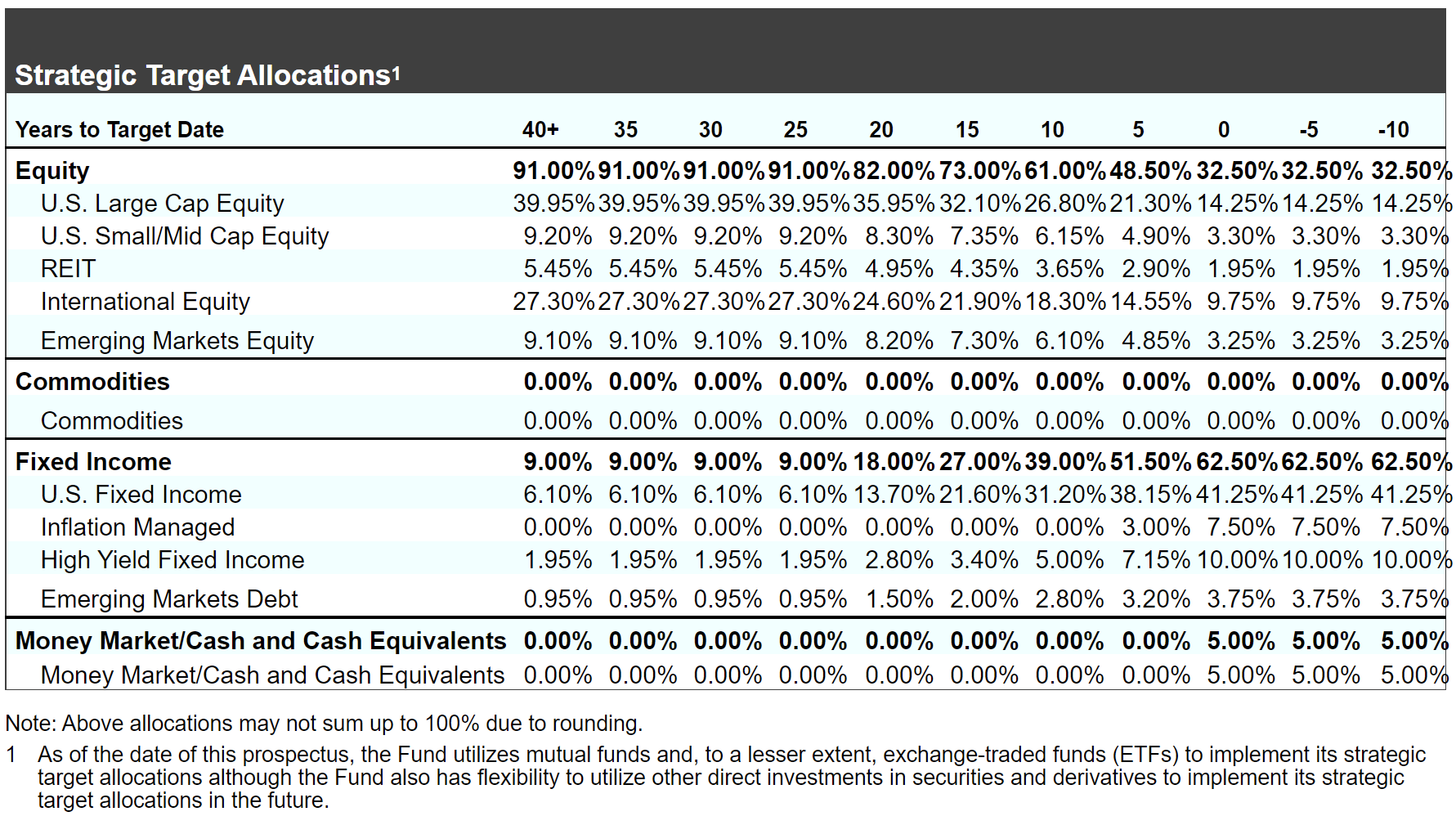
Notes of Explanation: Source: JPMorgan SmartRetirement Fund prospectus, November 1, 2021