The Bottom Line: Reports issued last week on climate change and related financial, economic, and social risks are required reading for investors and other stakeholders.
0:00
/
0:00
Listen to this article now
Carbon dioxide levels over time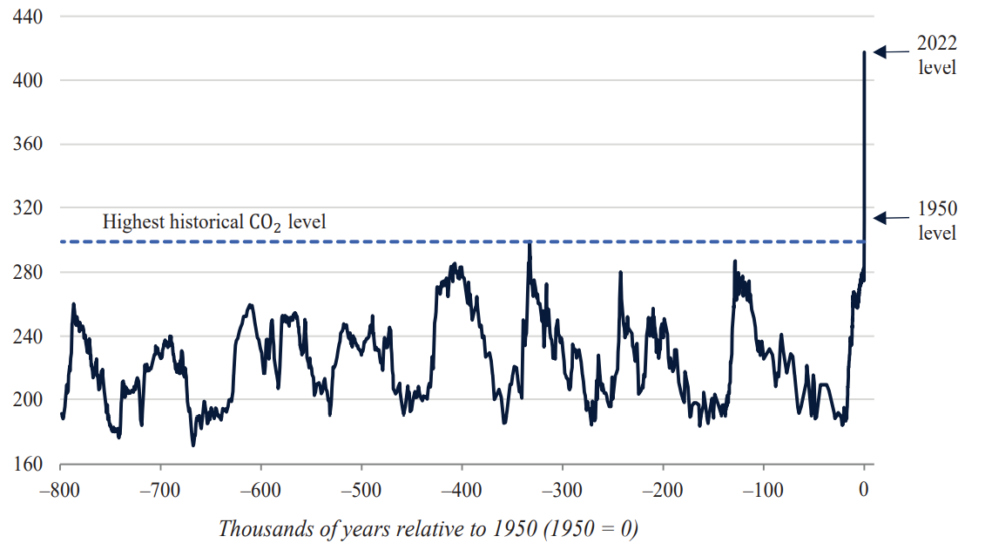 Notes of Explanation: Source: 2023 Economic Report to the President/Lüthi https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06949et al. 2008. Note: Data come from reconstructions from ice cores.
Notes of Explanation: Source: 2023 Economic Report to the President/Lüthi https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06949et al. 2008. Note: Data come from reconstructions from ice cores.
Observations:
- On top of President Biden’s veto of a bill passed by Congress that attempted to overturn a Department of Labor rule regarding consideration of ESG factors in the selection of investment options by retirement plan fiduciaries, including 401(k) plans, two consequential climate change-oriented reports with financial, economic, and social implications were issued last week on Monday that are required reading for all investors and other stakeholders. The first is a synthesis of six previous reports issued by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), a body of experts convened by the United Nations whose work is endorsed by 195 nations. The second is the annual 2023 Economic Report to the President, a document that devotes an entire chapter to climate change, along with a companion White Paper entitled “Methodologies and Considerations for Integrating the Physical and Transition Risks of Climate Change into Macroeconomic Forecasting for the President’s Budget.” The report warns of the resultant economic, financial, and social risks to the U.S. economy that will confront the Federal Government with related fiscal challenges.
- According to the IPCC synthesis report, human activities, principally through emissions of greenhouse gases, have caused surface temperatures to reach 1.1° Celsius and global average temperatures are estimated to rise to a level in excess of 1.5° Celsius above preindustrial levels sometime around the first half of the 2030s. Beyond that point, scientists believe that the impacts of climate change in the form of catastrophic heat waves, flooding, drought, crop failures and species extinction will reach a pivotal point that will be hard to reverse. There is still a 50/50 chance that the worst outcomes can be avoided, provided nations work together immediately to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by roughly 50% by 2030 and then stop adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere altogether by the early 2050s.
- The 2023 Economic report to the President warns that a warming planet poses severe economic challenges for the United States with consequences that would require the federal government to reassess its spending priorities. The report notes that even given ambitious action to rein in emissions that will be required to meet these national commitments, the climate will continue changing for the foreseeable future until global greenhouse gas emissions fall to zero.
- Considering these reports and their rather dire warnings regarding the potential impacts due to climate change, what are some actions that concerned investors may wish to consider, both negative and positive?
- First, investors in actively managed mutual funds and ETFs should investigate and understand the approach taken by their managers to factor climate change scenarios into their investment management processes. For some funds, relevant disclosures may be found in their Summary Prospectus, Prospectus and/or Statement of Additional Information. Other fund managers may disclose their sustainable investing practices on the firm’s website in the form of research reports or other disclosures. For investors working with financial advisers, an inquiry along these lines should be directed to their financial adviser.
- Second, investors in passively managed conventional funds may wish to consider switching to equivalent environmental, social and governance (ESG)-oriented, low cost ESG index funds, that account for relevant and material ESG risks but are also managed using strategies that involve investing in a representative sample of securities that collectively have an investment profile similar to that of an applicable underlying conventional index so as to limit tracking error. To ensure alignment with their sustainability preferences, investors should be aware of the methodology employed by the fund’s index to screen and monitor index constituents as well as the basis for excluding companies in certain industries, such as the extraction of thermal coal or the generation of electricity from thermal coal, or due to their engagement in controversial activities.
- Third, investors may also wish to consider an appropriate allocation, commensurate with their overall risk tolerance and investment time horizon, to one or more investment themes that will benefit from the opportunities of the clean energy transition. These include funds with a focus on the renewable energy sector, companies seeking to achieve net zero emissions, clean water and precious metals used in electric vehicles battery construction, to mention just a few. Green bond funds also fall into this category.